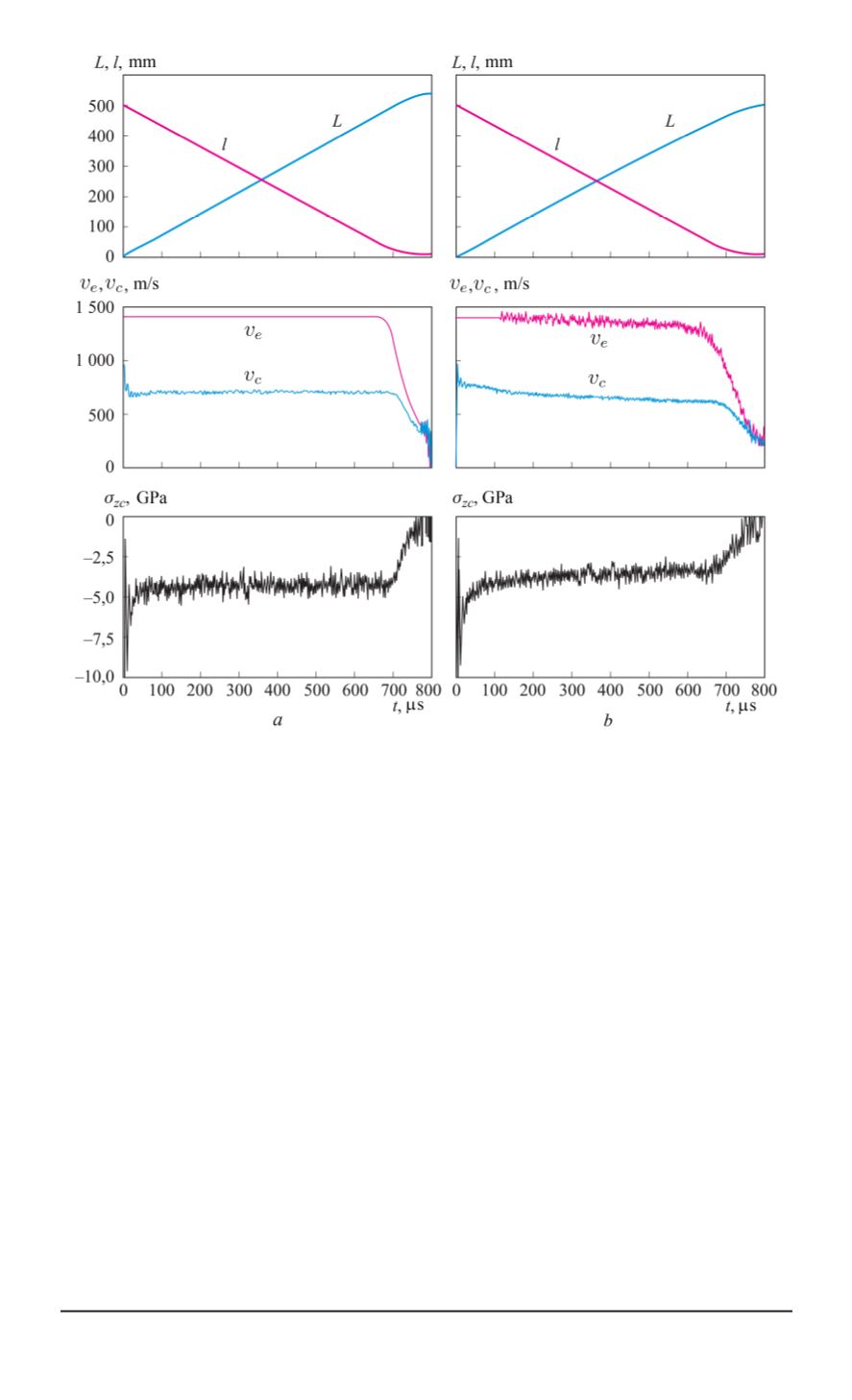
Fig. 5. Change of the parameters during the steel target penetration by the VNZh-
90 alloy rod with the yield strength of 50MPa (
a
) and 1500MPa (
b
) at the initial
interaction velocity of 1400m/s
cases a hydrodynamic penetration mode occurs when the projectiles “wear
away” completely as a result of their material spreading along the contact
boundary of the cavity formed in the target.
Fig. 5 and 6 illustrate the dynamical penetration of the VNZh-90 alloy
elongated projectiles used in the computations. It is illustrated by a time
ratio of the penetration depth
L
, a projectile current length
l
, a projectile
trailing end velocity
v
e
, a penetration velocity
v
c
, and an axial stress
σ
zs
on the contact border of the target constructed for the following
projectile initial velocities
v
0
and yield strength
σ
Y
values:
v
0
= 1400
m/s,
σ
Y
= 50
MPa (Fig. 5,
a
);
v
0
= 1400
m/s,
σ
Y
= 1500
MPa (Fig. 5,
b
);
v
0
= 2000
m/s,
σ
Y
= 1000
MPa (Fig. 6).
Comparison of the data in Fig. 5 shows a significant difference between
a dynamical behavior of the penetration parameters for the projectile with
a minimum strength (
σ
Y
= 50
MPa, see Fig. 5,
a
) and for a projectile with
a very high strength (
σ
Y
= 1500
MPa, see Fig. 5,
b
) at the same initial
velocity.
ISSN 0236-3941. HERALD of the BMSTU Series “Mechanical Engineering”. 2015. No. 1 77